Absolute pressure is the standard pressure at sea level amounts to 1.013 mbar[1 bar].
In practice the relative, or effective, pressure peff is of importance. This is the difference between the absolute pressure Pabs and the atmospheric pressure Pa :
Peff = Pabs – Pa
 The clearest reference pressure is the pressure zero, which exists in the air-free space of the universe. A pressure which is related to this reference pressure is known as absolute pressure. For the required differentiation from other types of pressure, it is denoted with the index “abs”, which is derived from the Latin “absolutus” meaning detached, independent.
The clearest reference pressure is the pressure zero, which exists in the air-free space of the universe. A pressure which is related to this reference pressure is known as absolute pressure. For the required differentiation from other types of pressure, it is denoted with the index “abs”, which is derived from the Latin “absolutus” meaning detached, independent.
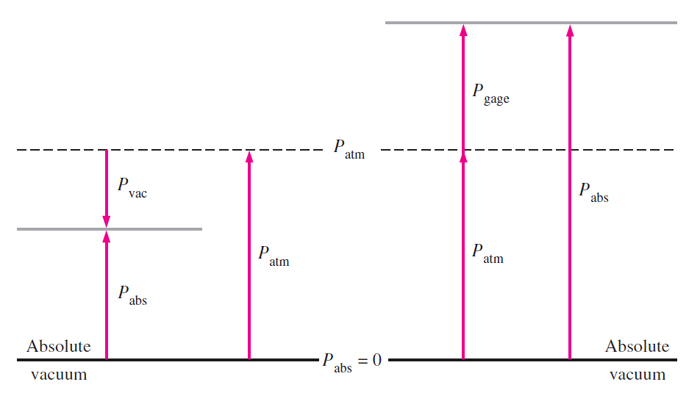
The absolute pressure it is measured relative to absolute vacuum (i.e., absolute zero pressure). Most pressure-measuring devices, however, are calibrated to read zero in the atmosphere and so they indicate the difference between the absolute pressure and the local atmospheric pressure. This difference is called the gage pressure. Pressures below atmospheric pressure are called vacuum pressures and are measured by vacuum gages that indicate the difference between the atmospheric pressure and the absolute pressure. Absolute, gage, and vacuum pressures are all positive quantities and are related to each other by
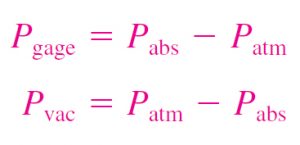
This is illustrated in below figure.
Like other pressure gages, the gage used to measure the air pressure in an automobile tire reads the gage pressure. Therefore, the common reading of 32 psi (2.25 kgf/cm2) indicates a pressure of 32 psi above the atmospheric pressure. At a location where the atmospheric pressure is 14.3 psi, for example, the Pabs in the tire is 32 + 14.3 = 46.3 psi.
| Example: What is the Pabs of a Vacuum Chamber?
A vacuum gage connected to a chamber reads 5.8 psi at a location where the atmospheric pressure is 14.5 psi. Determine the Pabs in the chamber. Solution The gage pressure of a vacuum chamber is given. The Pabs in the chamber is to be determined. Analysis The Pabs is easily determined Pabs = Patm – Pvac = 14.5 – 5.8 = 8.7 psi Discussion Note that the local value of the atmospheric pressure is used when determining the Pabs. |
